- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
what is the difference between casing and tubing?
Understanding the Difference Between Casing and Tubing in Oil and Gas Production
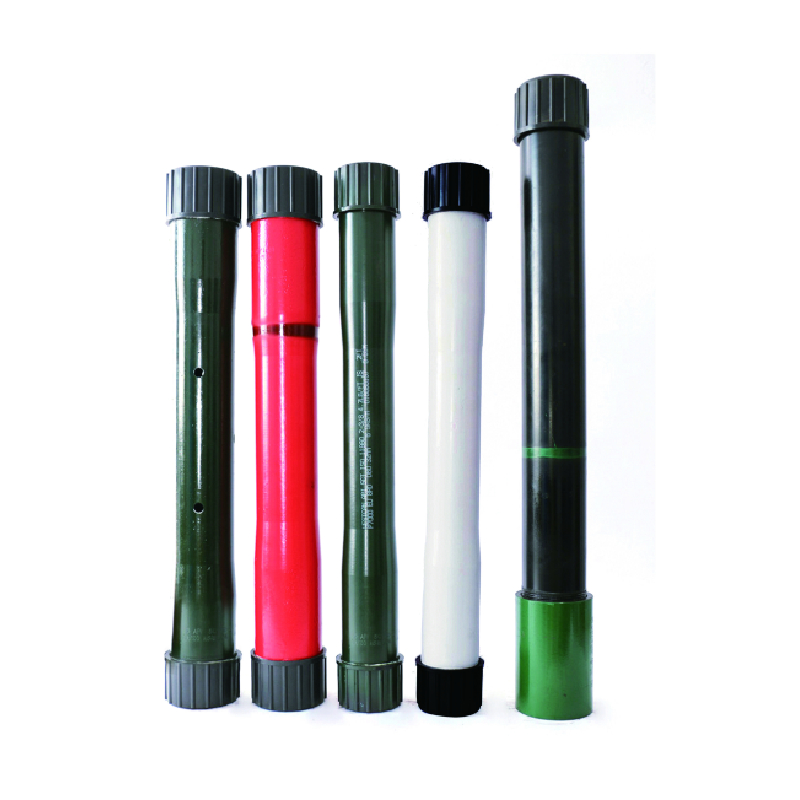
In the oil and gas industry, the terms casing and tubing are often used interchangeably by those outside the field, but they refer to two distinct components that play critical roles in the extraction of hydrocarbons from beneath the earth's surface. Understanding the differences between these two elements is essential for anyone looking to grasp the complexities of drilling and production processes.
Casing The Protective Layer
Casing is a series of steel pipes that are installed in a wellbore after the drilling process. Its main purpose is to stabilize the well and isolate different pressure zones, ensuring that the well maintains integrity throughout its lifespan. Casing serves several important functions
1. Well Integrity Casing helps to prevent the collapse of the wellbore, especially in unstable geological formations. It provides structural support and prevents the walls of the well from caving in during extraction activities.
2. Fluid Isolation The installation of casing separates the wellbore from surrounding formations, preventing the mixing of different fluids. This is crucial for managing pressures within the well and minimizing the risk of blowouts or uncontrolled flow situations.
3. Environmental Protection By isolating the well from shallow aquifers and other water sources, casing plays a significant role in minimizing the potential for contamination. This is essential for protecting both environmental resources and public health.
Casing is installed in sections, called “strings,” which are typically cemented in place to enhance their stability and sealing characteristics. Different types of casing exist depending on the well's depth, the nature of the formations being drilled, and regulatory requirements.
Tubing The Conduit for Production
what is the difference between casing and tubing?
In contrast, tubing refers to the inner conduit through which hydrocarbons flow from the reservoir to the surface once they have been extracted. Tubing is smaller in diameter and is installed inside the casing after the well has been completed. The key functions of tubing include
1. Production Flow Tubing is specifically designed to facilitate the flow of oil and gas from the reservoir to the surface. Its primary role is to transport the produced fluids efficiently and safely.
2. Pressure Management As production occurs, tubing helps manage the pressure within the well. It is engineered to withstand high pressures generated by the reservoir and the extracted fluids.
3. Enhanced Recovery Specialized tubing designs are often used to optimize recovery techniques, such as gas lift or artificial lift systems. In these cases, tubing plays a key role in injecting gas or other substances to enhance oil production.
Unlike casing, tubing is not cemented in place, allowing it to be replaced or serviced as needed during the life of the well. Regular maintenance and the potential for replacement are crucial for ensuring continuous production and optimizing performance.
Key Differences Summarized
The fundamental difference between casing and tubing lies in their purpose and function within the well. Casing is primarily concerned with structural support and environmental protection, while tubing is focused on facilitating the flow of hydrocarbons to the surface. Casing prevents external pressures from compromising the well integrity, whereas tubing manages the internal pressures and ensures efficient production.
In conclusion, both casing and tubing are integral to the successful extraction of oil and gas. Their distinct roles highlight the complexities of well engineering and the importance of proper installation and maintenance. Understanding these differences not only aids industry professionals but also informs stakeholders and the public about the safeguards and technologies employed in modern oil and gas production. As the industry continues to evolve with advancements in technology and environmental stewardship, the significance of these components will remain pivotal in ensuring safe and efficient energy extraction.
-
Tubing Pup Joints: Essential Components for Oil and Gas OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pup Joints: Essential Components for Reliable Drilling OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
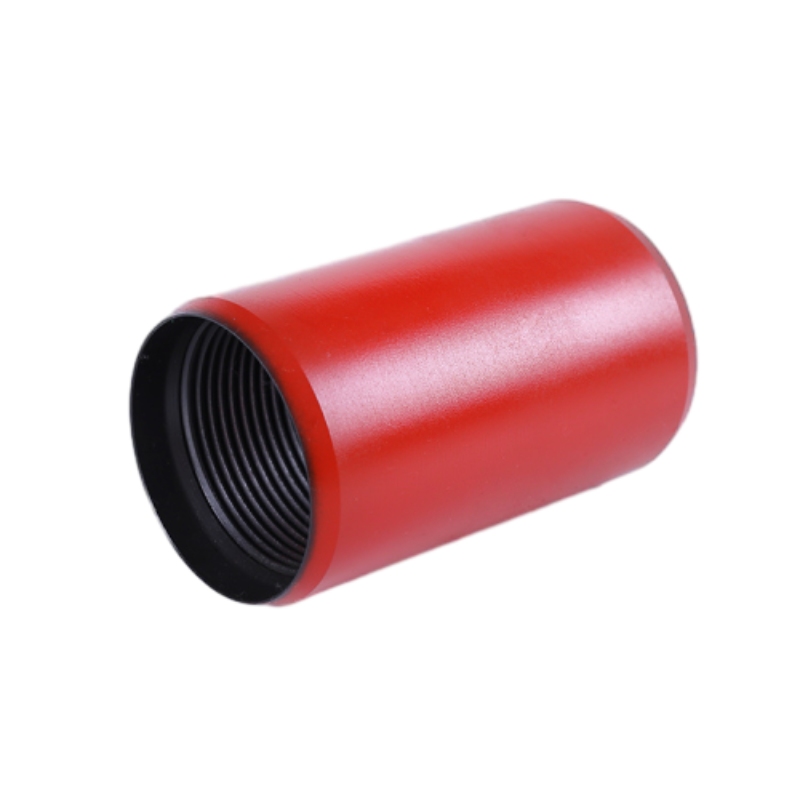
Pipe Couplings: Connecting Your World EfficientlyNewsJul.10,2025
-
Mastering Oilfield Operations with Quality Tubing and CasingNewsJul.10,2025
-
High-Quality Casing Couplings for Every NeedNewsJul.10,2025
-
Boost Your Drilling Efficiency with Premium Crossover Tools & Seating NipplesNewsJul.10,2025







