- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
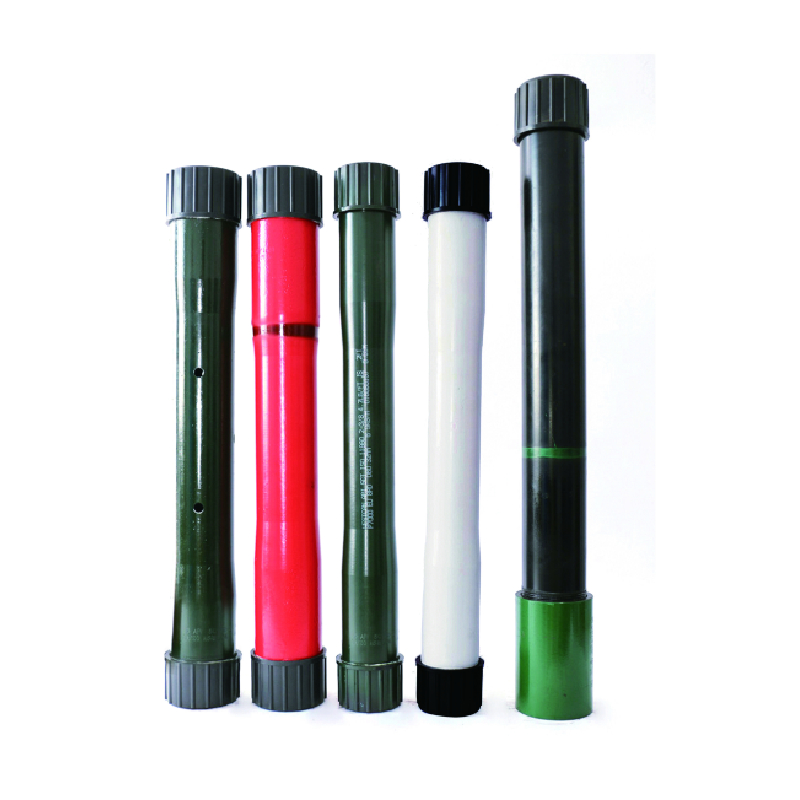
Understanding the distinctions between casing and tubing in oil and gas operations
Understanding the Difference Between Casing and Tubing in Oil and Gas Drilling
In the oil and gas industry, the terms casing and tubing are fundamental to the drilling and production processes. While both are pipes used in drilling operations, they serve distinct purposes and have different characteristics. Understanding the difference between casing and tubing is essential for anyone involved in petroleum engineering, drilling operations, or related fields.
What is Casing?
Casing refers to the large-diameter pipes that are installed in the wellbore (the hole drilled into the ground) to provide structural integrity and prevent the collapse of the well. Casing is inserted in phases during the drilling process and is cemented in place to create a seal. It serves multiple vital functions
1. Wellbore Stabilization Casing supports the walls of the wellbore, preventing collapses that could occur due to geological formations or pressure changes. It ensures that the well remains open and navigable for further operations.
2. Isolation of Fluids Casing also isolates different geological formations and groundwater sources, preventing fluid migration. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the well and protecting the surrounding environment from contamination.
3. Pressure Control The casing helps to control the pressure within the well, allowing engineers to manage risks related to high-pressure zones.
4. Facilitating Production Once the drilling phase is complete, casing allows for production activities, paving the way for the installation of production tubing.
What is Tubing?
Tubing, on the other hand, refers to the smaller-diameter pipes that are inserted inside the casing after drilling is complete. It acts as a conduit for oil or gas to flow from the reservoir to the surface. Tubing has specific characteristics that make it well-suited for production
1. Fluid Transport Tubing is designed specifically to transport fluids, including oil, gas, or water, from the wellbore to the surface. It ensures that the flow is efficient and minimizes pressure drops.
what is the difference between casing and tubing?
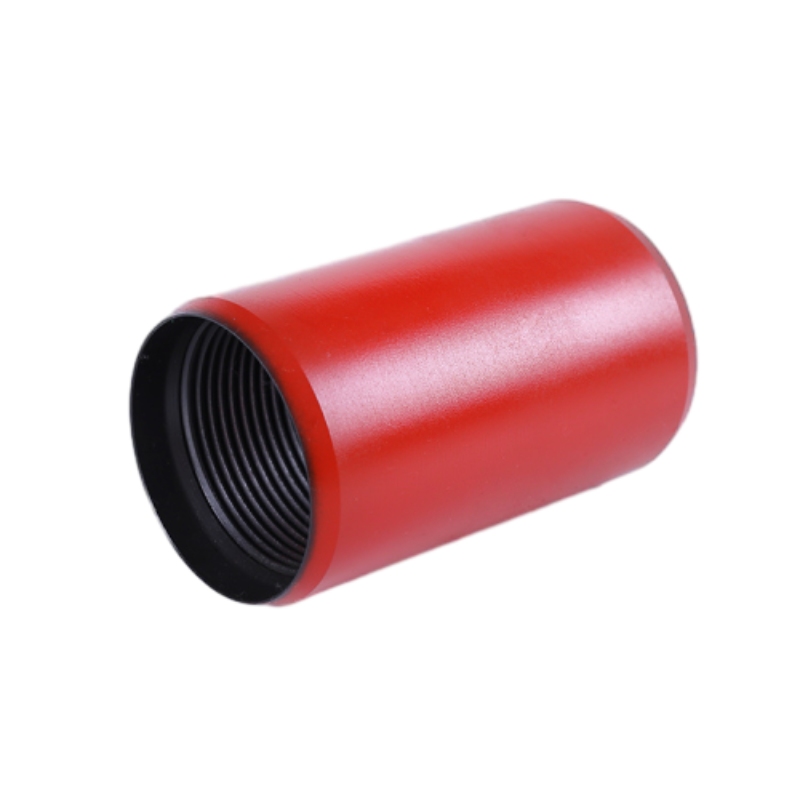
2. Higher Strength Requirements Tubing is subjected to varying pressures and temperatures during production, which necessitates higher strength materials that can withstand these conditions.
3. Ease of Maintenance Unlike casing, tubing can be removed or replaced without extensive drilling work. This feature allows for efficient maintenance and troubleshooting when production issues arise.
Key Differences Between Casing and Tubing
While both casing and tubing are essential components in the drilling process, their differences can be summarized as follows
1. Functionality Casing is primarily for wellbore stability and isolation, whereas tubing is used for production and transporting hydrocarbons to the surface.
2. Diameter Casing has a larger diameter than tubing, which is necessary for its role in supporting the well and preventing collapse.
3. Installation Casing is installed during the drilling phase, while tubing is installed after the drilling is completed and the well is ready for production.
4. Material Requirements Tubing requires more rigorous specifications and material standards due to its exposure to the harsh conditions of production, while casing materials are designed to handle wellbore support.
5. Removal and Replacement Tubing can be easily removed and replaced as needed, while casing remains in place indefinitely, serving its purpose throughout the life of the well.
Conclusion
In summary, both casing and tubing are critical components of well construction and operation in the oil and gas industry. Casing provides the necessary structural support and isolation for the wellbore, while tubing facilitates the efficient transport of hydrocarbons from the reservoir to the surface. By understanding the differences between these two types of pipes, professionals in the petroleum industry can ensure the safe and effective extraction of resources while maintaining environmental integrity.
-
Tubing Pup Joints: Essential Components for Oil and Gas OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pup Joints: Essential Components for Reliable Drilling OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pipe Couplings: Connecting Your World EfficientlyNewsJul.10,2025
-
Mastering Oilfield Operations with Quality Tubing and CasingNewsJul.10,2025
-
High-Quality Casing Couplings for Every NeedNewsJul.10,2025
-
Boost Your Drilling Efficiency with Premium Crossover Tools & Seating NipplesNewsJul.10,2025







