- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
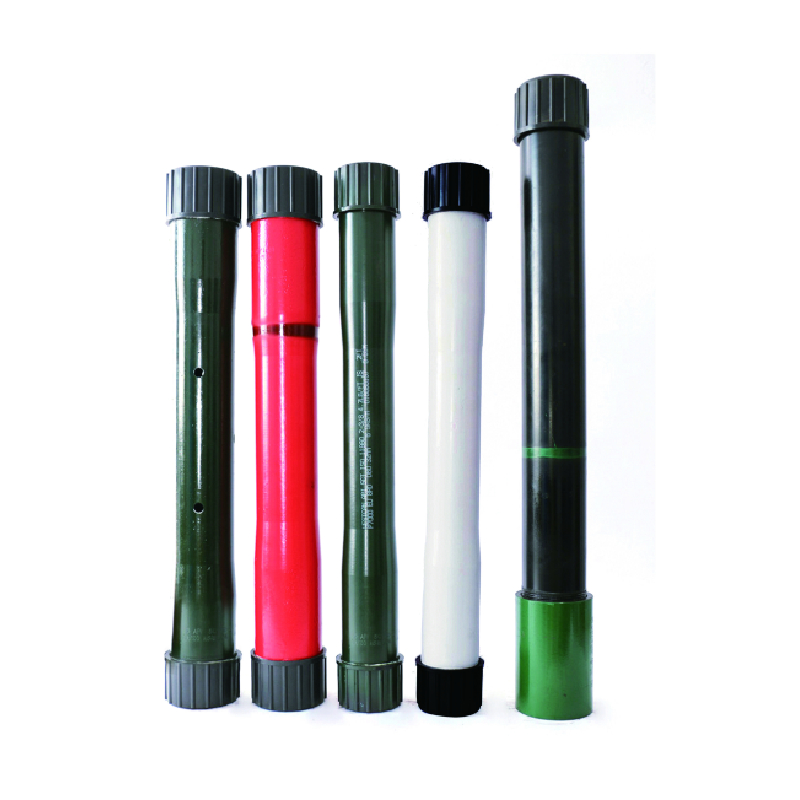
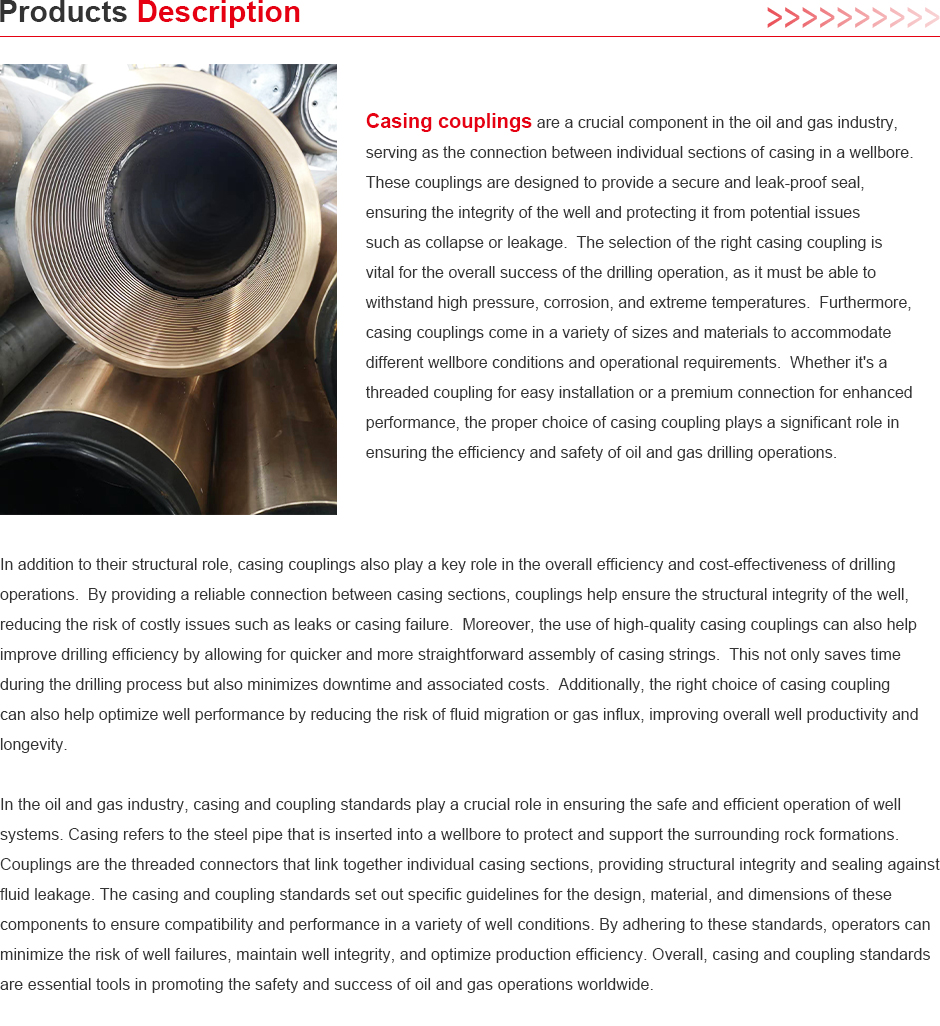
High Strength 3% and 4% Steel Couplings for Enhanced Durability and Performance
Understanding 3% 204% Steel Couplings Structure, Performance, and Applications
In the realm of mechanical engineering and construction, couplings play an essential role in connecting two shafts, enabling them to transmit torque while accommodating misalignment and protecting sensitive components. Among the various materials used for couplings, steel remains a popular choice due to its strength, durability, and versatility. One specific type of steel coupling that has garnered attention is the 3% 204% steel coupling.
Composition and Properties of 3% 204% Steel
The term 3% 204% steel often refers to a specific alloy composition that includes approximately 3% molybdenum and 2% chromium in conjunction with standard carbon steel properties. These alloying elements are added to enhance various mechanical properties, such as tensile strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance.
The addition of molybdenum helps improve the steel's strength at high temperatures and increases its hardenability, making it an ideal choice for applications that experience extreme conditions. Chromium, on the other hand, is known for its ability to improve corrosion resistance, especially when the coupling is exposed to moisture, chemicals, or other harsh environments.
Combined, these elements give 3% 204% steel couplings superior performance characteristics compared to standard carbon steel. They offer enhanced wear resistance and are capable of maintaining integrity under high-stress conditions, which makes them suitable for heavy-duty applications in various industries.
Design and Features
3% 204% steel couplings are designed with several features that enhance their functionality. They can come in different shapes and sizes, including rigid, flexible, and universal couplings, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
1. Rigid Couplings These couplings are designed to connect shafts that are perfectly aligned. They provide maximum torque transmission with minimal backlash, making them suitable for applications where high precision is required.
2. Flexible Couplings In situations where shafts may not be perfectly aligned, flexible couplings are used. They allow for some degree of movement, accommodating misalignment without compromising the integrity of the connection.
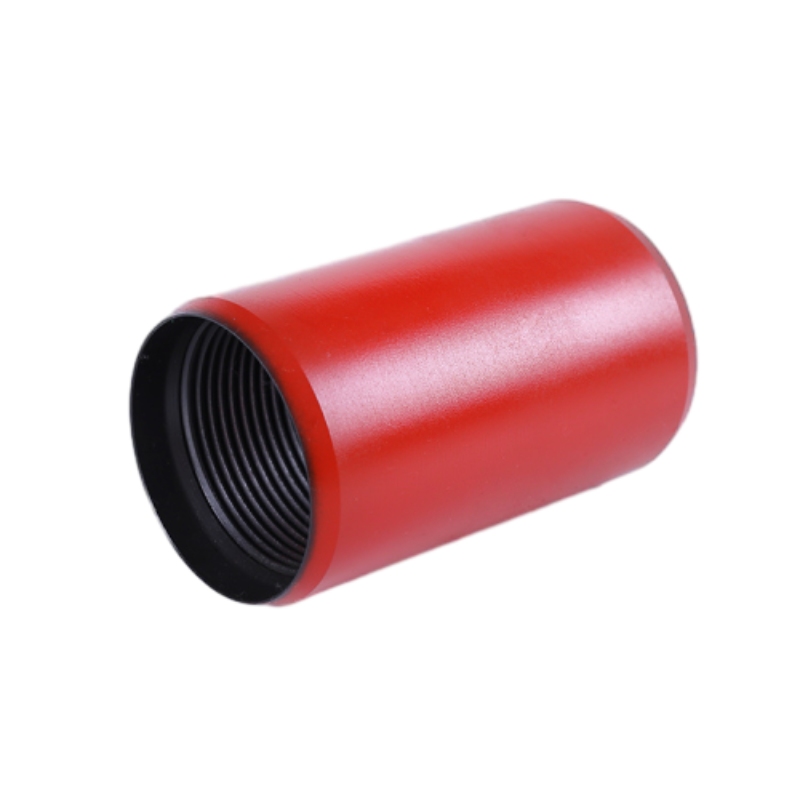
3 4 steel coupling
Each of these designs offers different advantages, and the choice among them largely depends on the specific application requirements, whether it is for automotive, industrial machinery, or robotics.
Applications in Various Industries
The robustness and reliability of 3% 204% steel couplings make them suitable for a wide range of applications
1. Automotive Industry In vehicles, these couplings are often used in drive shafts, helping to transfer torque from the engine to the wheels, ensuring efficient power delivery.
2. Manufacturing and Industrial Machinery Couplings are fundamental components in various machinery, including conveyor systems and pumps, where they link the motor to the driven component.
3. Robotics In robotic systems, where precise movement and feedback are critical, 3% 204% steel couplings can provide reliable torque transmission while accommodating slight variances in alignment.
4. Aerospace Applications The high strength-to-weight ratio of 3% 204% steel makes it an excellent choice for aviation components that need to withstand significant forces while keeping overall weight manageable.
Conclusion
In summary, 3% 204% steel couplings represent a vital component in modern engineering, offering unique properties that enhance performance across various applications. Their combination of strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion allows industries to optimize machinery and improve overall efficiency. Whether in automotive, manufacturing, robotics, or aerospace, the role of couplings cannot be understated. As engineers continue to push the boundaries of technology, the demand for specialized materials like 3% 204% steel will undoubtedly grow, solidifying its place in the toolbox of mechanical design and innovation.
-
Tubing Pup Joints: Essential Components for Oil and Gas OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pup Joints: Essential Components for Reliable Drilling OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pipe Couplings: Connecting Your World EfficientlyNewsJul.10,2025
-
Mastering Oilfield Operations with Quality Tubing and CasingNewsJul.10,2025
-
High-Quality Casing Couplings for Every NeedNewsJul.10,2025
-
Boost Your Drilling Efficiency with Premium Crossover Tools & Seating NipplesNewsJul.10,2025







