- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Understanding Bull Plug Pressure Ratings for Safe Drilling Operations
Understanding Bull Plug Pressure Ratings
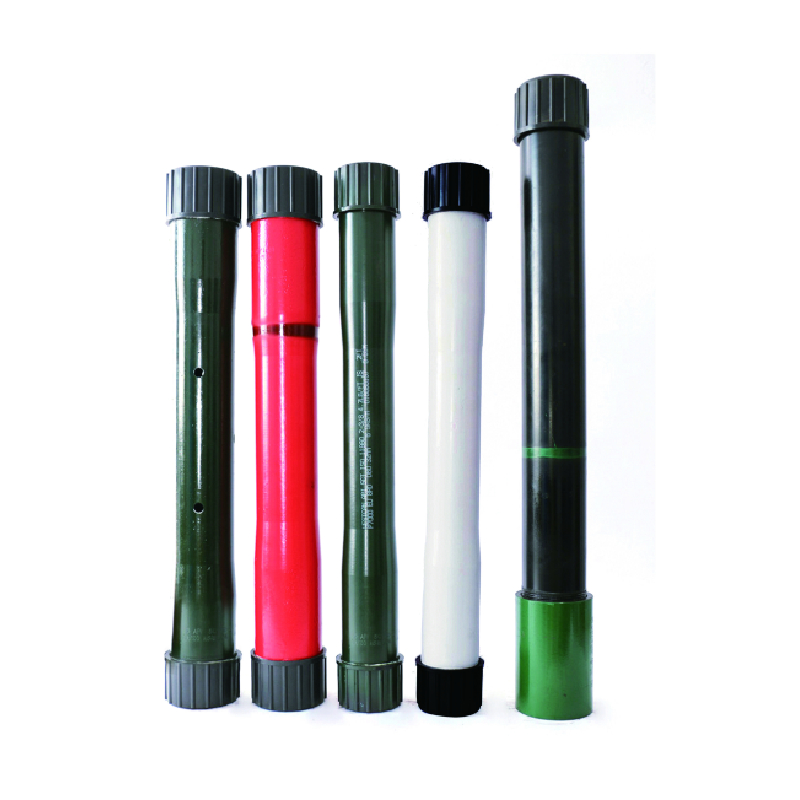
In the world of industrial equipment and piping systems, the bull plug plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and efficiency. A bull plug is a type of pipe plug used to seal off the ends of pipes, preventing the escape of fluids or gases. Properly understanding its pressure rating is essential for preventing leaks, ensuring system integrity, and averting potential hazards.
Understanding Bull Plug Pressure Ratings
The pressure rating is typically denoted in pounds per square inch (PSI) or bar. For instance, a common pressure rating for a carbon steel bull plug might be 150 PSI, while a stainless steel plug may be rated for higher pressures, such as 300 PSI or more. Understanding these ratings is vital when selecting a bull plug for specific applications. Using a plug beyond its rated capacity can lead to catastrophic failures, including leaks, bursts, or the ejection of the plug itself.
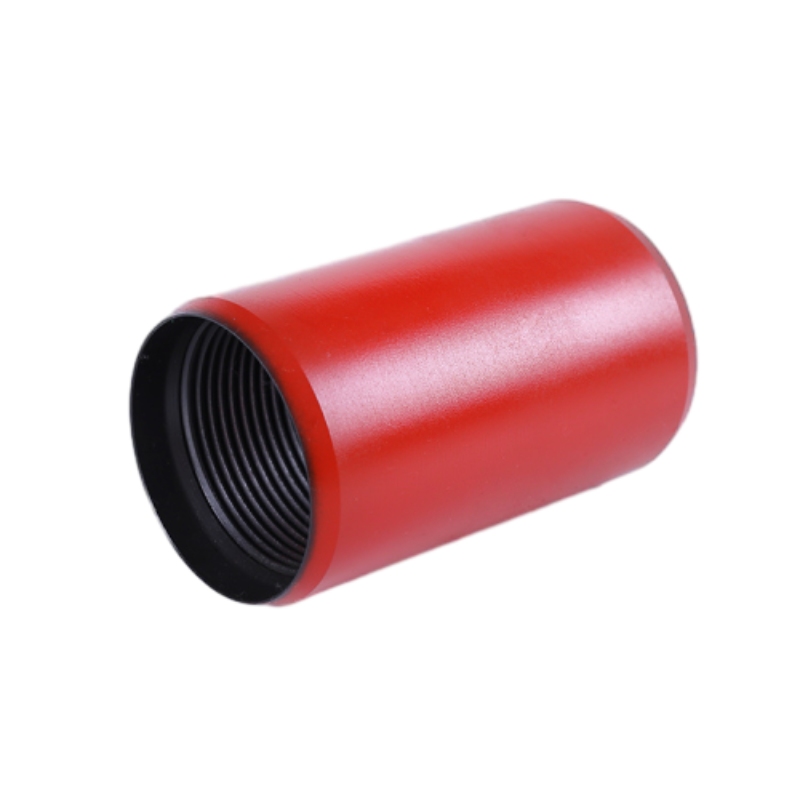
bull plug pressure rating
In addition to the material and its pressure rating, other factors must be considered when selecting a bull plug. These include temperature ratings, compatibility with various chemicals, and the environment in which the plug will be used. For example, high-temperature applications may necessitate plugs made of materials that can withstand thermal expansion and contraction without losing their sealing capability.
Moreover, industry standards and certifications play a significant role in ensuring that bull plugs meet specific performance criteria. Organizations such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) provide guidelines and standards that manufacturers must adhere to, ensuring the reliability and safety of their products.
In summary, understanding bull plug pressure ratings is essential for anyone involved in the design, maintenance, or operation of piping systems. A failure to recognize the significance of these ratings can have dire consequences in terms of safety and operational efficiency. When selecting a bull plug, always consider its material, pressure rating, operating conditions, and industry standards to ensure a successful and safe application. Knowledge and diligence in these areas are key to preventing costly accidents and promoting a safe working environment.
-
Tubing Pup Joints: Essential Components for Oil and Gas OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pup Joints: Essential Components for Reliable Drilling OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pipe Couplings: Connecting Your World EfficientlyNewsJul.10,2025
-
Mastering Oilfield Operations with Quality Tubing and CasingNewsJul.10,2025
-
High-Quality Casing Couplings for Every NeedNewsJul.10,2025
-
Boost Your Drilling Efficiency with Premium Crossover Tools & Seating NipplesNewsJul.10,2025







