- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
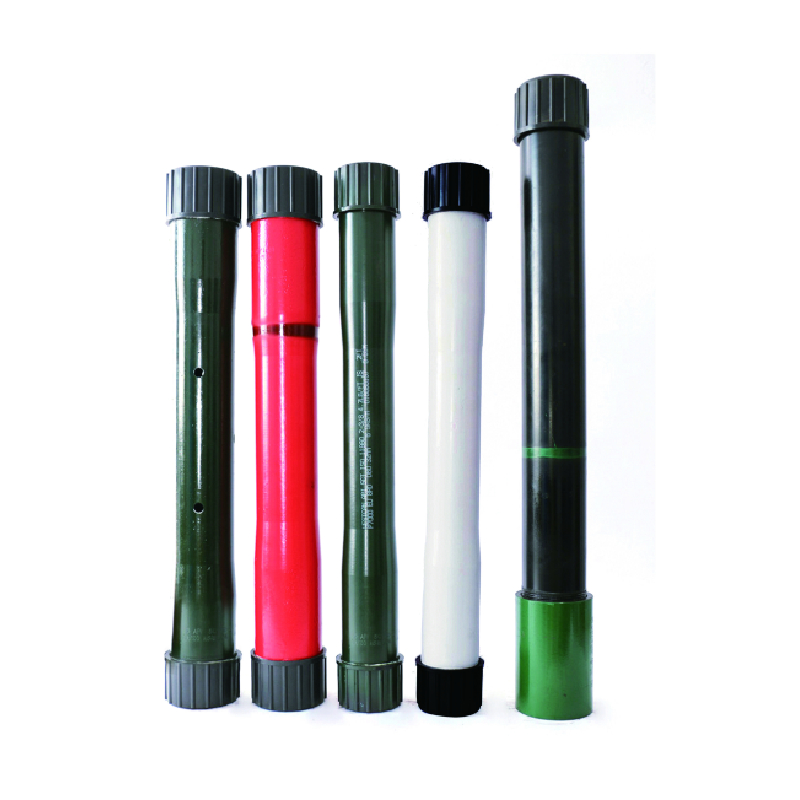
casing and tubing connections
Casing and Tubing Connections An Overview
Casing and tubing are critical components in the oil and gas industry, serving as the backbone for maintaining well integrity and ensuring safe operations. The process of drilling a well involves several phases, each requiring specific types of materials and connections to secure the wellbore against various geological and operational challenges. This article delves into the different types of casing and tubing connections, their importance, and the advancements in technology that enhance their performance.
The Purpose of Casing and Tubing
Casing is a series of steel pipes that are installed in the well bore after drilling to provide structural support. It keeps the well open and protects the formation from collapse. Tubing, on the other hand, is a smaller diameter pipe that allows oil and gas to flow from the reservoir to the surface. The effective functioning of both casing and tubing is crucial for well productivity and the prevention of environmental hazards.
Types of Casing Connections
Casing connections can be broadly categorized into two types threaded and welded.
1. Threaded Connections These are popular due to their ease of installation and disassembly. The most common type is the API (American Petroleum Institute) threaded connection, which consists of a tapered thread. They are designed to provide a tight seal and withstand the pressures encountered during drilling and production. However, threaded connections are susceptible to galling, where the threads can wear down or seize up, especially under high-stress conditions.
2. Welded Connections Welding provides a strong and permanent bond between casing sections. It eliminates the potential for thread damage and can handle higher pressure conditions. However, once welded, these connections are not meant to be disassembled without cutting, which can complicate repairs or modifications.
Types of Tubing Connections
casing and tubing connections
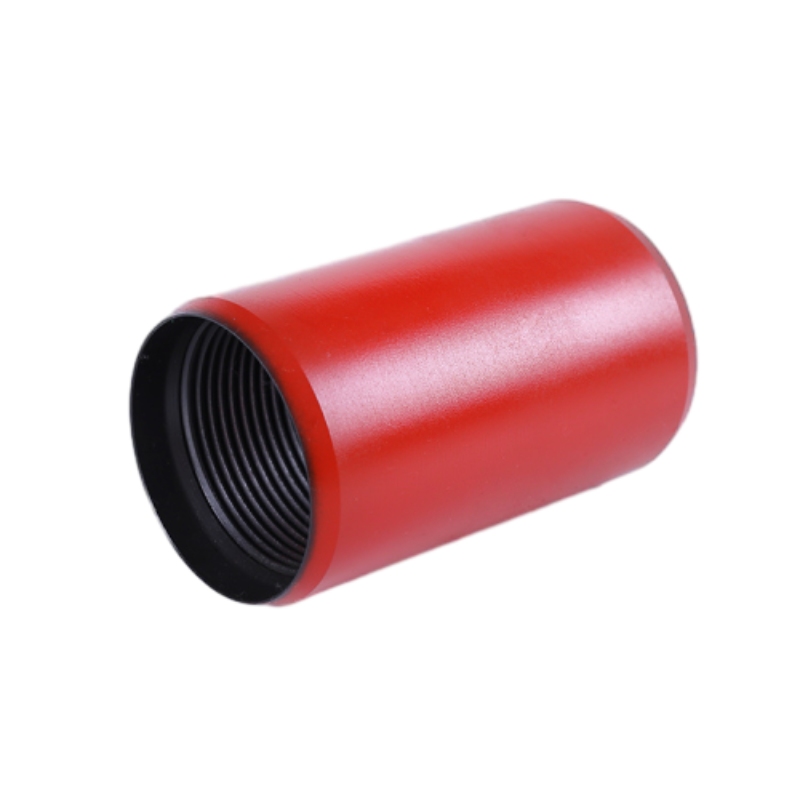
Like casing, tubing connections can also be categorized into threaded and welded types, with variations tailored to meet specific operational needs.
1. API Tubing Connections Just like API casing, API tubing utilizes a threaded connection that allows for easy assembly. New advancements include improved threading profiles to enhance the strength and resistance to wear.
2. Premium Connections These are engineered to offer superior performance and reliability, especially in challenging environments. They are often used in deep-water drilling and high-pressure applications. Premium connections incorporate advanced designs that boast enhanced sealing capabilities and considerable resistance to bending and torsion forces.
Advancements in Connection Technology
The oil and gas industry has seen significant advancements in connection technology, leading to improved performance and safety. One such advancement is the introduction of non-metallic materials in casing and tubing connections, which can offer better corrosion resistance and lower weight. Additionally, innovations in connection designs have led to self-locking mechanisms and enhanced seal integrity, thus reducing the risk of leaks and blowouts.
Furthermore, the adoption of automated and robotic technologies during installation ensures higher precision and significantly reduces the risk of human error. These technologies enable the monitoring of connections in real time, facilitating early detection of potential issues before they escalate.
Conclusion
Casing and tubing connections are integral to the successful operation of oil and gas wells. Understanding their types and the technological advancements surrounding them is essential for optimizing well performance and ensuring safety. As the industry continues to evolve, embracing new materials and technologies will play a vital role in addressing the challenges posed by increasingly complex well environments. The focus on developing robust and reliable connections will remain paramount, safeguarding both productivity and the surrounding environment in the pursuit of energy resources.
-
Tubing Pup Joints: Essential Components for Oil and Gas OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pup Joints: Essential Components for Reliable Drilling OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pipe Couplings: Connecting Your World EfficientlyNewsJul.10,2025
-
Mastering Oilfield Operations with Quality Tubing and CasingNewsJul.10,2025
-
High-Quality Casing Couplings for Every NeedNewsJul.10,2025
-
Boost Your Drilling Efficiency with Premium Crossover Tools & Seating NipplesNewsJul.10,2025







