- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Exploring the Benefits and Applications of 2% Bull Plug in Various Industries and Settings
Understanding the 2% Bull Plug A Practical Guide
The phrase 2% bull plug may seem obscure at first glance, but it refers to a critical component in various industries, particularly in fluid dynamics and pneumatic systems. The term “bull plug” indicates a type of blind plug used to seal openings in pipes or equipment. When specified with a percentage (such as 2%), it often refers to the size or internal pressure rating of the fitting, which is crucial for maintaining system integrity and efficiency.
What is a Bull Plug?
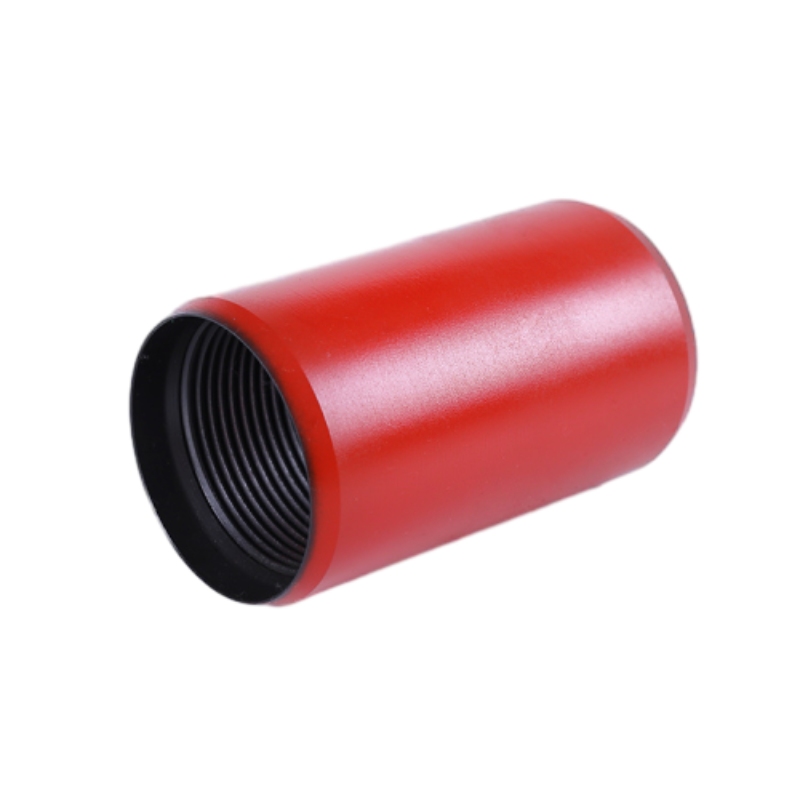
A bull plug is a type of fitting designed to close off openings in piping systems. Unlike other plugs that might allow flow in one direction, bull plugs completely block the passage of fluids or gases. This capability makes them essential for maintenance tasks, ensuring that systems can be serviced without risking leaks or fluid loss. They are often used alongside valves and other fittings in pipelines, tanks, and pressure vessels.
Importance of the 2% Rating
The 2% specification in a bull plug may refer to the tolerance level or allowable deviation in manufacturing. For instance, in industries where precision is crucial, a bull plug rated for a very tight tolerance—such as 2%—can significantly contribute to the seamless operation of a system. A tighter tolerance minimizes the risk of leaks or failures, especially in high-pressure applications where safety is paramount.
Moreover, the 2% specification may also relate to the pressure rating of the fitting, where it indicates that the bull plug can effectively handle pressures up to 2% above or below a certain level. This rating aids engineers and technicians in selecting the right components for their applications, ensuring they can withstand the operational stresses they will encounter in real-world conditions.
Applications of Bull Plugs
2 bull plug
Bull plugs, including those specified with a 2% rating, are versatile components used in various industries. In the oil and gas sector, they are critical for sealing off segments of pipelines during maintenance, preventing spills that could have disastrous environmental consequences. In manufacturing plants, bull plugs are used in pneumatic systems to block off unused ports and maintain system pressure even when certain sections are not in operation.
Additionally, in water distribution systems, bull plugs are essential for testing and isolating sections of pipe, ensuring that repairs can be done safely without disrupting service. Even in HVAC systems, these plugs can be important for sealing off portions of ductwork or pumps to optimize airflow and energy efficiency.
Choosing the Right Bull Plug
When selecting a bull plug for your application, consider key factors such as material compatibility, pressure rating, size, and the specific requirements of your system. Materials like stainless steel, plastic, and brass offer various advantages depending on the environment and the media flowing through the system. For example, stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for harsh environments, while plastic may be more appropriate for lighter applications.
Furthermore, always consult technical specifications and guidelines provided by manufacturers to ensure that the selected bull plug meets the necessary qualifications for your application. Failure to do so might lead to costly repairs, safety hazards, and operational inefficiencies.
Conclusion
The 2% bull plug is a seemingly simple yet vital component in numerous fluid and gas handling systems. Understanding its specifications, including the importance of ratings, material choices, and applications, can significantly enhance your operational efficiency and safety. Whether in oil and gas, manufacturing, or water systems, the proper use of bull plugs ensures that these systems function smoothly and securely. Investing time in selecting the appropriate fittings can contribute to the longevity and reliability of your operations.
-
Tubing Pup Joints: Essential Components for Oil and Gas OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pup Joints: Essential Components for Reliable Drilling OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pipe Couplings: Connecting Your World EfficientlyNewsJul.10,2025
-
Mastering Oilfield Operations with Quality Tubing and CasingNewsJul.10,2025
-
High-Quality Casing Couplings for Every NeedNewsJul.10,2025
-
Boost Your Drilling Efficiency with Premium Crossover Tools & Seating NipplesNewsJul.10,2025







