- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
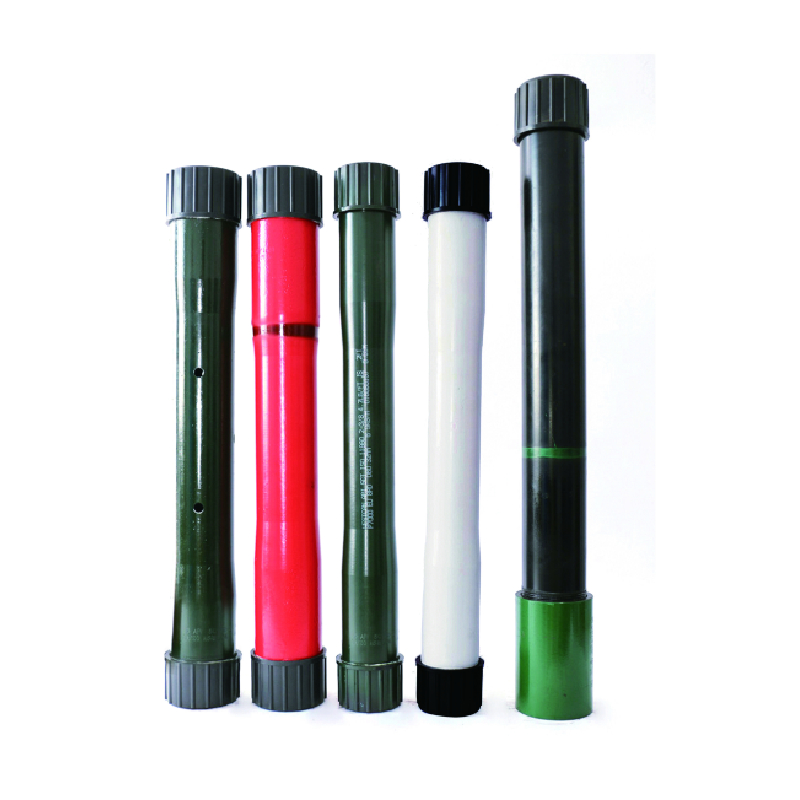
stainless steel coupling 1 2
Understanding Stainless Steel Couplings A Focus on Type 1 and Type 2
Stainless steel couplings are essential components in various industrial applications, providing a reliable and durable means to connect piping systems, shafts, and other mechanical parts. This article will explore the significance of stainless steel couplings, particularly focusing on Type 1 and Type 2 couplings, their features, applications, and advantages.
What is a Stainless Steel Coupling?
A coupling is a device that connects two shafts together for the purpose of transmitting power. In the context of piping systems, a coupling serves as a connector that allows two pipes to be combined, facilitating the flow of fluids or gases. Stainless steel is often the material of choice due to its corrosion resistance, strength, and durability, making it particularly suited for harsh environments and applications.
Types of Stainless Steel Couplings
When discussing stainless steel couplings, we often categorize them into different types. Here, we will examine Type 1 and Type 2 couplings, both of which have distinct characteristics and uses.
Type 1 Couplings
Type 1 couplings are primarily designed for applications that require flexibility and the ability to absorb misalignments. These couplings typically feature a flexible design, allowing them to accommodate angular misalignment between two shafts or pipes. This flexibility is particularly valuable in situations where vibrations are present, as it helps reduce wear and tear on connected components.
Type 1 couplings are often used in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and marine applications, where the alignment of components may not always be perfect. Their ability to handle shocks and vibrations makes them a reliable choice for dynamic environments.
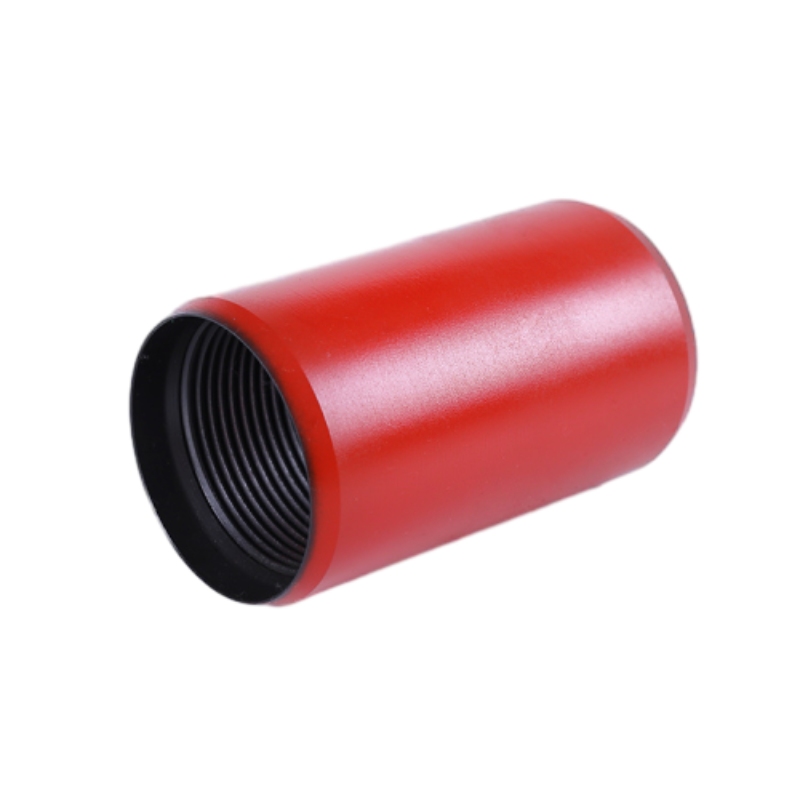
Type 2 Couplings
Type 2 couplings, on the other hand, are engineered for strength and rigidity. These couplings are designed to handle high torque and provide a solid connection between components. Often used in scenarios where precise alignment is critical, Type 2 couplings excel in static applications like conveyor systems, heavy machinery, and industrial HVAC systems.
stainless steel coupling 1 2
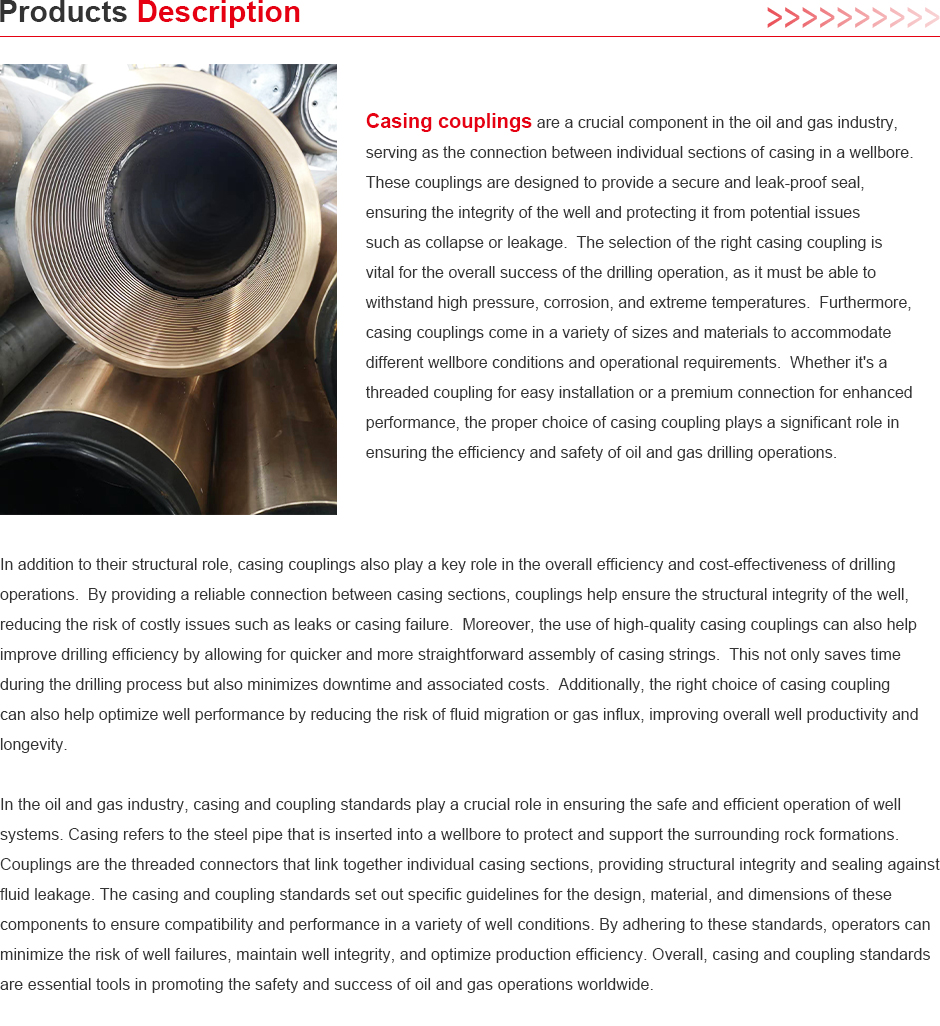
The robust construction of Type 2 couplings makes them ideal for applications subject to high loads and pressure. They may not accommodate misalignment as effectively as Type 1 couplings, but their durability and strength make them a preferred choice in demanding environments.
Advantages of Stainless Steel Couplings
Both Type 1 and Type 2 stainless steel couplings carry several advantages that enhance their appeal in industrial and commercial settings
1. Corrosion Resistance Stainless steel is highly resistant to rust and corrosion, making it suitable for use in wet or chemically aggressive environments.
2. Durability These couplings can withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical stress, leading to a longer lifespan and reduced maintenance costs.
3. Versatility Available in various sizes and designs, stainless steel couplings can be customized to meet specific application requirements.
4. Easy Installation Couplings typically feature designs that facilitate straightforward installation and replacement, minimizing downtime during maintenance activities.
5. Hygienic Properties In industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals, stainless steel's non-porous surface helps maintain hygiene standards, preventing contamination.
Conclusion
Stainless steel couplings, particularly Type 1 and Type 2, are invaluable components across various industries. Their unique attributes—flexibility and rigidity—allow them to serve different purposes effectively. Whether handling vibrations and misalignments or providing robust connections under high torque, these couplings play a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency and longevity of mechanical systems. Understanding the differences and applications of Type 1 and Type 2 stainless steel couplings is vital for choosing the right solution for your specific needs. Investing in high-quality stainless steel couplings means investing in durability, functionality, and reliability in your operations.
-
Tubing Pup Joints: Essential Components for Oil and Gas OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pup Joints: Essential Components for Reliable Drilling OperationsNewsJul.10,2025
-
Pipe Couplings: Connecting Your World EfficientlyNewsJul.10,2025
-
Mastering Oilfield Operations with Quality Tubing and CasingNewsJul.10,2025
-
High-Quality Casing Couplings for Every NeedNewsJul.10,2025
-
Boost Your Drilling Efficiency with Premium Crossover Tools & Seating NipplesNewsJul.10,2025







